
In the intricate world of medical device manufacturing, precision is very important. Lives depend on the accuracy and reliability of these devices, from minimally invasive surgical tools to complex implantable components. Among the array of manufacturing techniques available, metal laser cutting has emerged as a cornerstone, offering unparalleled precision, versatility, and efficiency. This blog delves into the intricacies of medical device metal laser cutting, exploring its benefits, applications, and the technological advancements driving its evolution.
Applications: Where Metal Laser Cutting used in Medical Devices
The applications of metal laser cutting in medical device manufacturing are vast and ever-expanding:

- Stents: Laser cutting is indispensable for creating intricate stent designs, including coronary stents, vascular stents, and esophageal stents. The precise cuts ensure optimal expansion and flexibility, crucial for successful implantation.
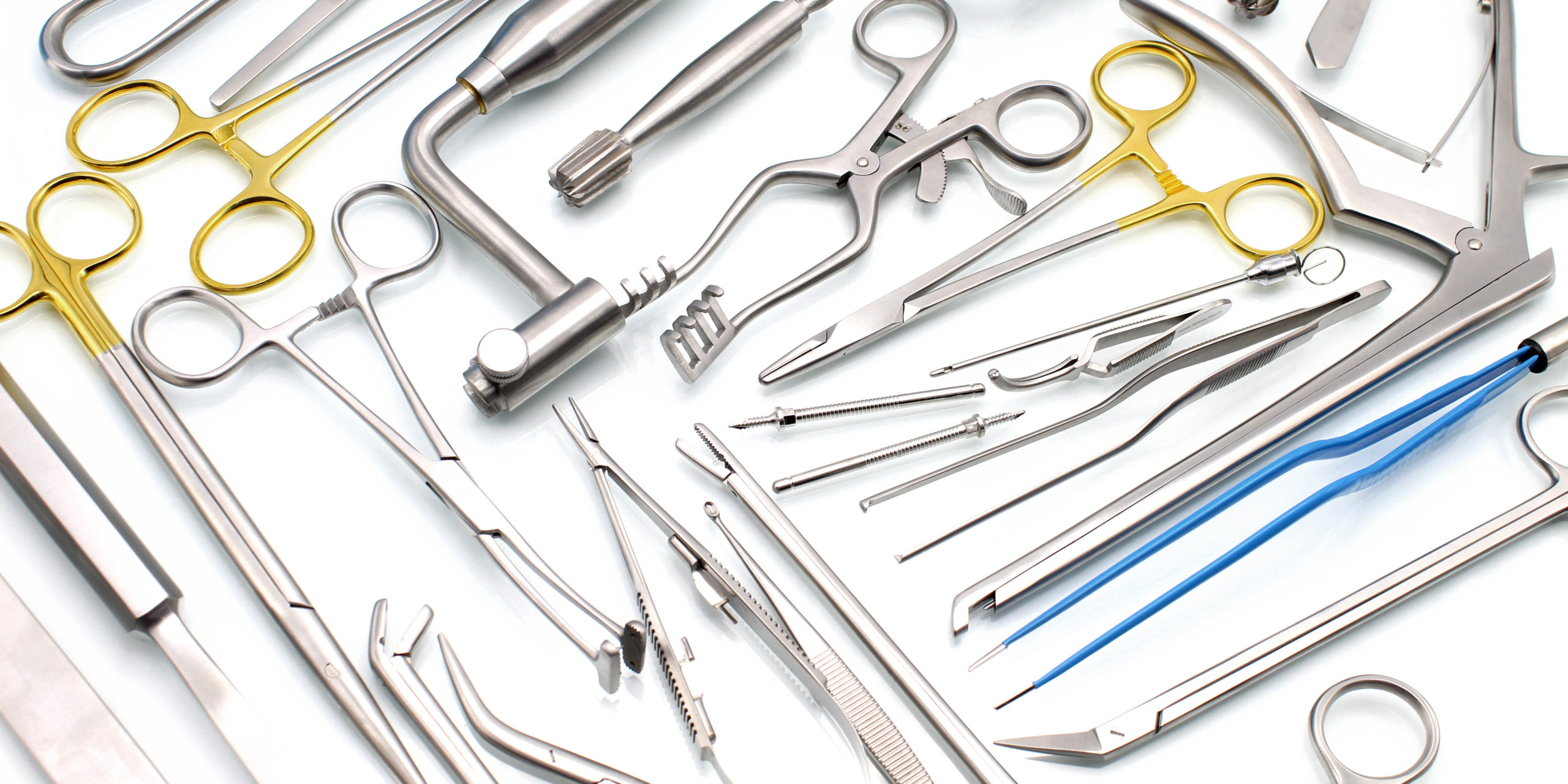

2. Surgical Instruments: Laser cutting is used to manufacture a wide range of surgical instruments, such as scalpels, forceps, scissors, and endoscopic tools. The ability to create sharp, precise edges and complex shapes enhances surgical accuracy and minimizes tissue damage.
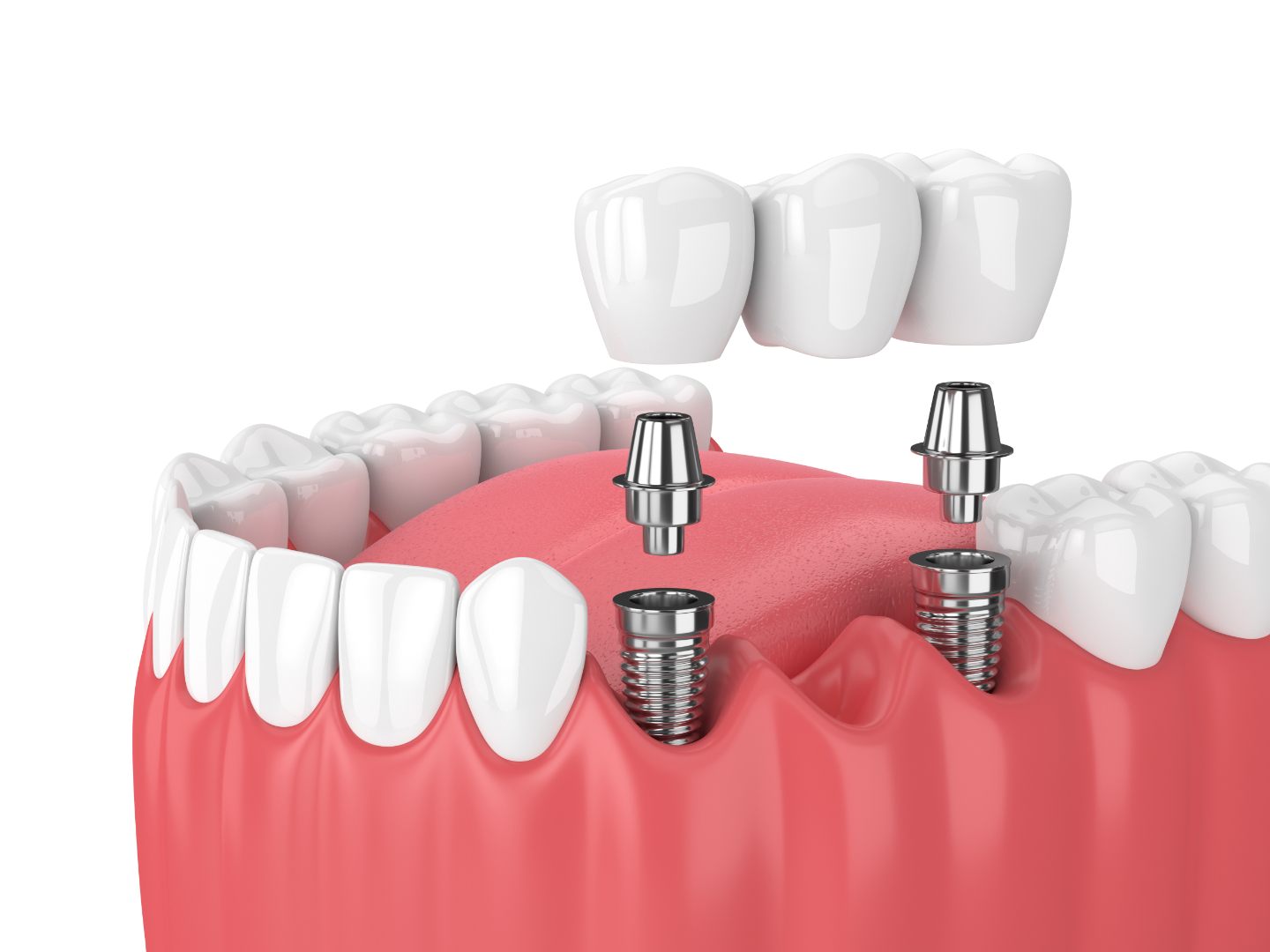
3. Implants: Laser cutting plays a crucial role in manufacturing orthopedic implants, such as bone plates, screws, and joint replacements. The precise geometries and smooth surfaces ensure proper fit and integration with surrounding tissues.
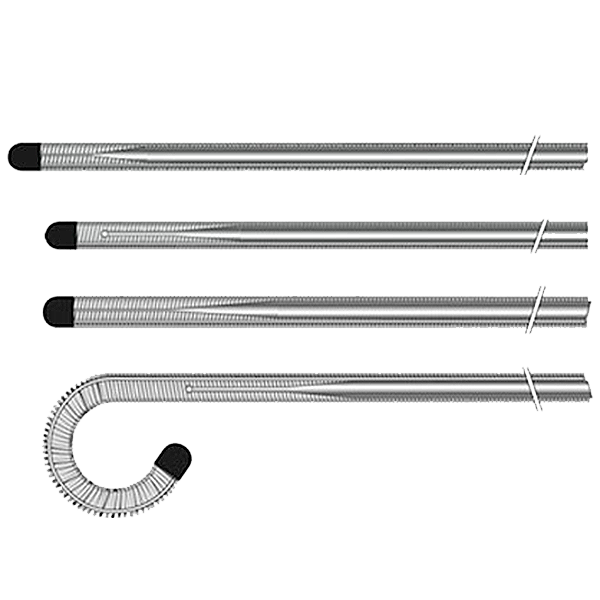
4. Catheters and Guidewires: Laser cutting is used to create intricate features in catheters and guidewires, such as side holes, slots, and tapers. These features are essential for fluid delivery, navigation, and device deployment.
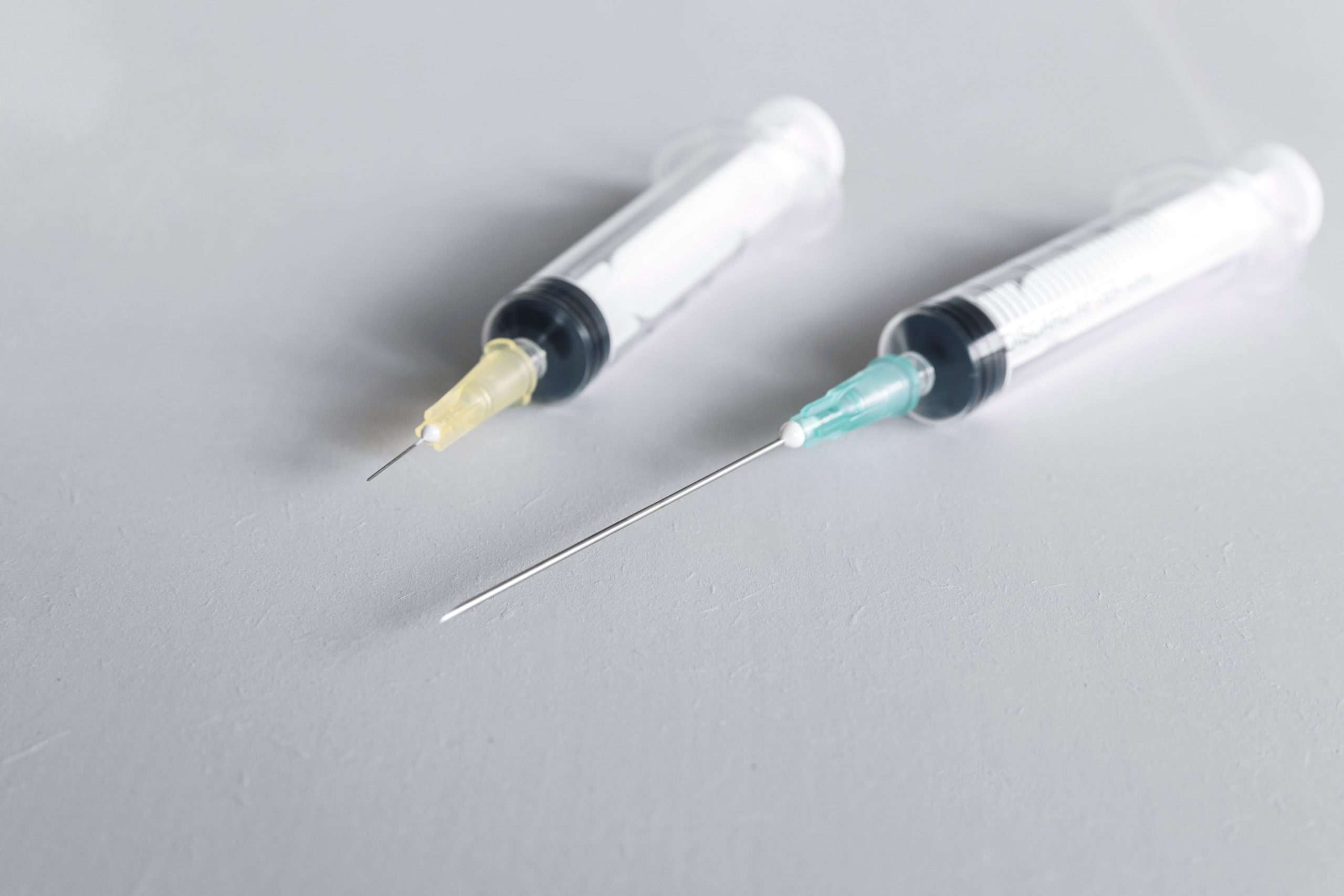
5. Needles and Cannulas: Laser cutting enables the production of ultra-fine needles and cannulas with precise bevels and sharp tips, minimizing patient discomfort and ensuring accurate drug delivery.
Why Metal Laser Cutting Reigns Supreme in Medical Device Manufacturing
The adoption of laser cutting in the medical device industry is driven by a confluence of factors:
- Unmatched Precision: Laser cutting offers exceptionally tight tolerances, crucial for the miniaturization and intricate designs common in medical devices. The ability to achieve micron-level accuracy ensures that components fit together perfectly and function as intended.
- Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Compared to traditional cutting methods, laser cutting generates a smaller HAZ, minimizing thermal damage to the surrounding material. This is particularly important for biocompatible metals, as excessive heat can alter their properties.
- Non-Contact Process: Laser cutting is a non-contact process, eliminating mechanical stress on the workpiece. This is essential for delicate and fragile materials, preventing deformation and ensuring structural integrity.
- Versatility and Flexibility: Laser cutting can handle a wide range of metals and thicknesses, making it suitable for diverse applications. It also allows for rapid prototyping and design modifications, accelerating the development cycle.
- Clean and Burr-Free Cuts: Laser cutting produces clean, burr-free cuts, reducing the need for secondary finishing operations. This not only saves time and cost but also minimizes the risk of contamination.
- High Throughput and Efficiency: Advanced laser systems offer high cutting speeds and automated processes, enabling efficient production of large volumes of components.
Understand How Metal Laser Cutting Machine Works
Fiber Laser cutting, at its core, is a thermal process that utilizes a highly focused laser beam to melt, vaporize, or ablate material. In the context of medical devices, this technique is employed to create intricate shapes, precise cuts, and complex geometries in a variety of metals, including stainless steel, titanium, nitinol, and precious metals.
The process typically involves:
- Beam Generation: A laser source, such as a fiber laser or CO2 laser, generates a highly concentrated beam of light.
- Beam Delivery: The beam is directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to focus it onto the workpiece.
- Material Interaction: The focused laser beam interacts with the metal, causing it to melt or vaporize.
- Assist Gas: An assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, is often used to remove molten material and protect the cut edge from oxidation.
- CNC Control: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems precisely control the laser beam’s movement, ensuring accuracy and repeatability.
